Water Ionization
Electrolysis re-organizes the water:
The process of electrolysis breaks water into smaller units, which can penetrate cells much more efficiently than normal water. The “Ionized” Water is freshly re-organized water which penetrates the cells at a much faster rate for better nutrient absorption and more efficient waste removal. Smaller water units also have a positive effect on the efficiency of the metabolic processes. Then how the ionization affect the molecular structure of water is that Water that enters the electrolytic cell is subjected to a small electric current which passes between the plates, causing the water molecules [H2O] to split into two ions: a negatively charged hydroxyl ion [OH-] and a positively charged hydrogen ion [H+].
Therefore Water already is capable of undergoing both oxidation and reduction, releasing oxygen at the anode (positive electrode),
H2O → ½ O2 (g) + 2 H+ + 2 e– E° = –1.23 v
and reduction, producing hydrogen gas at the cathode ( negative electrode )
2 H2O + 2 e– → H2 (g) + 2 OH– E° = -0.83 v
Thus if an aqueous solution is subjected to electrolysis, one or both of the above reactions may be able to compete with the electrolysis of the solute. For example, if we try to electrolyze a solution of sodium chloride, hydrogen is produced at the cathode (negative electrode) instead of sodium:
anode: Cl– → ½ Cl2(g) + e– E° = –1.36 v
net: Cl– + H2O → 2 H2(g) + ½ Cl2(g) + 2 OH– E = –0.95 v
Benefits of Water Ionization (Electrolysis)
aKua® is a brand name of KTCC’s Water Ionizer. It comes from aQua + alKaline Water.
STEP 1: FILTRATION
Water enters the ionizer through an inlet port the unit and is first filtered to remove common pollutants, particulate matter, chlorine, odor and organic matter present in tap water.
STEP 2: ELECTROLYSIS [ Water Ionization ] The water then flows through an electrolysis chamber which contains positively and negatively charged platinum-covered titanium electrodes. These electrodes ionize the soluble minerals in the water: positively charged ions gather at the cathode (negative electrode) to create alkaline water, also referred to as “reduced water” while negatively charged ions gather at the anode (positive electrode) to make acid water, also known as “oxidized water”.
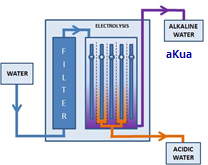
• ACIDIC WATER, which is dispensed through the bottom hose or spout, is used externally for cleaning and disinfecting the skin and household surfaces. It is discharged into the sink when it is not needed or saved for later use.
Water that enters the electrolytic cell is subjected to a small electric current which passes between the plates, causing the water molecules [H2O] to split into two ions: a negatively charged hydroxyl ion [OH-] and a positively charged hydrogen ion [H+].
At the exit of the electrolytic cell, the water is separated into two streams:
• The alkaline water stream contains a larger proportion of hydroxyl ions [OH-] which act as a powerful antioxidant, or reducing agent, because these ions have spare electrons that can easily be donated to our cells. Antioxidants neutralizes the oxidative damage caused by electron scavenging free radicals in our body.
• The acidic water stream contains a larger proportion of hydrogen ions [H+] which, contrary to hydroxyl ions, act as a oxidant or good for skin cleaning.

Follow Social